What should be in host. What is a hosts file? Rules for editing the hosts file
Hosts - a text file containing a database of domain names and used when they are translated into network addresses of hosts. Requests to this file take precedence over requests to DNS servers. Unlike DNS, the content of the file is controlled by the computer's administrator. All of the above means that with the help of this file you can very easily and simply configure access to any of the existing Internet resources. Let's say you want to block access to one of the popular social networks, for example, . To do this, you only have to write a few lines in hosts and save the changes. After that, any user who used your computer will simply not be able to get into VK, since access will be denied. Of course, with a set of minimal knowledge, this prohibition is easily bypassed.
The average user should theoretically not know anything about the hosts file, since he simply does not need it. Alas, modern realities are such that we have to learn a lot of new things. The fact is that in the past few years, a lot of fraudulent organizations have appeared that use hosts to steal personal information, as well as to take money from a person by redirecting him to other sites for the purpose of extortion. For you to understand what I'm talking about, I'll give you an example. Let's say you decide to go to the same VK. Only instead of your page you see a warning in which you are asked to send SMS to a short number in order to make sure that you are a real person and not a robot. The reasons may be different, in this case it does not matter. You send a message, after which money starts to be debited from your account. This is the scam you have become a part of. You must immediately call your telecom operator, explain the situation and ask for a refund to the account. Most likely, you will have to write a written statement, after which the funds will be returned to you, since they were illegally withdrawn from the account.
How could this happen? Using the hosts file, you are automatically redirected to a fraudulent site, which only appearance resembles the usual VKontakte, while the address in the line can be real (that is, vk.com). However, this is not VK. To verify this, you can open hosts and see extra lines like 111.222.333.333 vk.com, with the help of which the redirect occurs.
Another question arises - how can hosts change? Yes, it's very simple: for this you just need to bring a Trojan to your PC, which will do the whole operation without your knowledge. And you can pick it up on almost any site.
So, now let's move on to the main question, namely: what does the file look like? I will say right away that it differs slightly depending on the operating system.
Windows XP

# Copyright (c) 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp.
#
#
#space.
#
#
# For example:
#
127.0.0.1 localhost
Windows Vista

#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhost
Windows 7 and 8

# Copyright (c) 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
As you can see, the files practically do not differ from each other for some difference. However, for each operating system, I recommend using a different hosts. Just copy the specified data.
By the way, the files are located in the following sections:
- On Windows XP/2003/Vista/7/8 C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
- On Windows NT/2000: C:\WINNT\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
If you do not have the ability or desire to change this file yourself, you can use the utility called, which I recently talked about - it automatically changes the contents of hosts if it contains extra characters.
What is the Hosts file for?
The purpose of this system file is to assign certain IP addresses to certain site addresses.
This file is very fond of all kinds of viruses and malware in order to write their data into it or simply replace it.
The result of these actions may be signs of "inserting" the site into browsers, which will ask to send SMS when the browser is opened, or blocking various sites, at the discretion of the creators of the virus.
Where is the hosts file in windows?
For different versions of Windows, the location of the hosts file is slightly different:
Windows 95/98/ME: WINDOWS\hosts
Windows NT/2000: WINNT\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
Windows XP/2003/Vista/Seven(7)/8: WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts
And the ending hosts, this is already the target file, not the folder. He doesn't have .
What should the correct hosts file look like?
The "content" of the hosts file is also slightly different for different windows versions, but not much. It is "written" in English for what it is needed and how to make exceptions with one example. All lines that begin with a # sign mean that they are commented out and do not affect the file.
The contents of the original hosts file for Windows XP:
#
#
#space.
#
#
# For example:
#
127.0.0.1 localhost
Contents of the original hosts file for Windows Vista:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
127.0.0.1 localhost::1 localhost
The contents of the original hosts file for Windows 7:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
The contents of the original hosts file for Windows 8:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
As you can see, the contents of the host file for different versions windows, there are no special differences.
How to open and edit the hosts file?
The hosts file can be found in standard Windows Notepad.
This is probably the most interesting part of the article.
First of all, you need to understand why change this file at all? Yes, in order to deny access to certain sites. Thus, by changing this file and writing the site address into it, the user will not be able to access it through any .
In order to change the hosts file, it is advisable to open it as an administrator () by right-clicking on the file and selecting "Run as administrator". Or open Notepad in this way and open the file in it.
For quick action, you can simply click the Start button and select Run ( win+r) () and enter in the line:
notepad %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts

This will open the file in Notepad.
In order to block access to the site(suppose it will be test.ru ), you just need to add a line with this site to the very bottom:
127.0.0.1 test.ru
As a result, the file will have the following content:
# Copyright (c) 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# This HOSTS file created by Dr.Web Anti-rootkit API
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# ::1 localhost
127.0.0.1 test.ru
Each new site that you want to block, you need to start on a new line and write, not forgetting the local IP address 127.0.0.1
Also, to edit the hosts file, there is a program HOSTS EDITOR, which you can download and read the description from.
The principle of her work is that she helps to edit the hosts file.
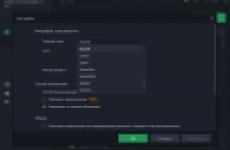
From the screen below, the principle of its operation is clear, everything is done in a couple of clicks. Adding is done by clicking on + .

After editing, do not forget to click on the save button (2 "Save changes" button to the left of the "+" button).
You can also change this file for good purposes, for example speed up website loading.
How it works?
When you enter the site, you see its domain name, which has letters. But all sites on the Internet have an IP address, and the names are already assigned using DNS. I will not go into the details of this process, the article is not about that. But here you need to know that the hosts file has priority when accessing sites, and only after it is a DNS request.
In order to speed up the loading of the site, you need to know its IP address and domain.
The IP address of a site can be found using various services, for example, or.
Domain is the name of the site.
For example, let's speed up the loading of this site on which you are reading an article by explicitly specifying the IP address and domain for the file.
Then the added line will be:
91.218.228.14 site
This speeds up page loading in a couple of seconds, and can sometimes give access if standard means You cannot access the site.
More with possible redirect to another site using the hosts file.
To do this, you need to know the IP address of the site and its domain (as in the case described above), then the added line will be like this:
91.218.228.14 test.ru
And now, after entering the site test.ru into the address bar of the browser, you will be redirected to the site specified in the IP address..
If you want to clean hosts file, then you can do this by simply deleting the content and inserting the original text into it, from the description above (under the spoilers).
Some nuances in host file s:
Thus, you can easily and free of charge block access to sites in Windows by editing the hosts file.
Hi all! Yesterday I spent the whole evening on Skype, helping a friend solve the problem of why VKontakte does not open for him. The answer lay almost on the surface, but as is usually the case in such cases, we stubbornly ignored it. The whole trick was that a friend, working on his site in Denver, opened Contact (with Denver running, respectively), after which he turned off the computer without turning off Denver. And as a result, in the hosts file, VKontakte signed up with a local ip. Therefore, today, having seized a minute, I decided to write another post, devoting it to the hosts file. In this article, we will talk about what the hosts file does, what it is for, how to find it, how to edit and save it. Also, at the very bottom of the article, you can download the hosts file. I will try to describe everything in simple human language, so that even an amateur who is not particularly versed in computers can understand.
What's happenedhosts? The hosts file is a text file on your device with Internet access (computer, smartphone, etc.). The hosts file contains a database of domain names. Every time you write a particular site address in your browser, the hosts file is initially requested, and then only the DNS (external servers located on the Internet) is accessed. And if you forbid this or that address in the hosts file, then it will be impossible to access it from this computer. That, perhaps, is all that the hosts file does.
How to find a filehosts? The hosts file is located in different places on different operating systems. Below is a table of how it can be found in the most popular operating systems
Everything below, until the next paragraph, is dedicated to those who do not know what to do with this table. And so, if for you this is Filkin's letter, written in Chinese, then most likely you have Windows. Here, based on this OS, I will explain how to find the hosts file.
We go to My computer. Click on the address bar (see screenshot) and paste this phrase there: C:\Windows\system32\drivers\etc . This is the path to the hosts file. Then press Enter.
We get into the system folder. Find the hosts file. Everything! You can congratulate yourself, you are a computer genius! 😉

If you have any problems, or you have a different axis, and you do not know what and how to do, then write in the comments, I will be happy to answer. And we're moving on.
How to open a filehosts? Since we have found the hosts file, now we need to somehow open it. There is nothing complicated in this. Opens hosts with any text editor. I use Notepad++ but you can open it with any other. Even the usual Notepad, which is built into Windows by default.
What should be in the hosts file? Nothing extra. But seriously, a clean hosts file should look like this:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp. # # This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. # # This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each # entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should # be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. # The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one # space. # # Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual # lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol. # # For example: # # 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server # 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself. # 127.0.0.1 localhost # ::1 localhost
If you are squirting in English, then, as you can see, the file itself says in detail what the hosts file does, what it should contain and how to change it. I also want to remind you that at the end of the article you can download the hosts file, so there is no need to copy it from here.
But, the fact that you will see just such a file is unlikely. Most likely, there will be other lines in your hosts file. For example, if you use Adobe products, then at the end you will find something like:
127.0.0.1 adobe-dns.adobe.com 127.0.0.1 adobe-dns-2.adobe.com 127.0.0.1 adobe-dns-3.adobe.com
And now, let's move on to the most interesting:
Editinghosts. And so, now we will learn how to change the hosts file. First, let's understand what certain symbols mean in it. It is very easy, at the level of the first grade (my student goes to the second grade, edits this file once or twice).
Anything marked with a "#" is a comment. We do not take them into account. Those. you can put "#" and write whatever you want. This will not be taken into account by the computer. But, as soon as you move to a new line, if you do not put "#" again, the computer will begin to take into account your line. Let's go again, the line with the "#" is a comment, and is not taken into account by the computer.
Desert lines in hosts are ignored. You need to put them only for your convenience, so as not to get confused later.
The numbers 127.0.0.1 are the local ip address. What is ipadres, it is necessary to write a whole article. Therefore, for now, the main thing for us to remember is that any Internet address after 127.0.0.1 will be ignored, and you will not be able to access it on the Internet.
For example, having a line like:
127.0.0.1 google.ru
You will not be able to access the Google search engine. Thus, it is possible to deny access to any site, just by entering the url of the unwanted site after the local ip address.
These lines must be entered at the end of the file. Each new site address must start on a new line.
Sometimes it happens that some programs change this file, mostly Virtual Servers or viruses. But, if virtual servers return hosts to their original state after they are closed, then viruses maliciously edit hosts. In any case, the result is the same: you cannot get to a particular site. Therefore, if you cannot access a site, check the hosts file, it may be that access is denied in it.
Now I will reveal one terrible secret. Social networks and some other sites are often blocked at work. Often, AI silencers block in exactly the way described above. But, you already know how to change the hosts file 😉
By the way, if you want to prevent your child from accessing certain sites, then you can easily edit the hosts file by specifying the addresses of unwanted resources in it. As a result, your hosts file will look like this:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp. # # This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. # # This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each # entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should # be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name. # The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one # space. # # Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual # lines or following the machine name denoted by a "#" symbol. # # For example: # # 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server # 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host # localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself. # 127.0.0.1 localhost # ::1 localhost 127.0.0.1 Enter the address of the site you want to block 127.0.0.1 Enter the address of the site you want to block 127.0.0.1 Enter the address of the site you want to block
Everything, after we have edited the hosts file, we can safely save it.
Windows is far from Linux in terms of the systematic use of configuration files in order to customize the functionality of the operating system. First of all, because Windows uses the registry for this.
But nevertheless, there are such files in Windows, and sometimes it is useful to know about their purpose. An important repository of configuration options is a file called Hosts. The file name does not have an extension, so you do not need to specify it during automatic search.
In the course of the presentation, we will focus on the OS of the seventh version, as the most massively used by consumers (Microsoft's tricks in the G8 failed to convince users that Metro is cool).
In fact, we are dealing with a repository of domain names, similar to the names of DNS servers. The benefit of using it is that the computer owner is able to regulate the priorities of domains when they are translated into real network addresses when accessing Internet resources.
File domains take precedence over any external DNS addresses, even those specified in the network connection settings. The default storage location in the "seven" is as follows: %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\hosts. However, this path is not possible. The system administrator can override it by changing the registry key named HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters\DataBasePath. Files with the same name and purpose are included not only in the Windows system environment, they can be found in Unix-like operating systems, in Mac-OS, and even on the Android platform.
Internal Structure of Hosts Records and Storage Manipulation
Although Hosts has no extension, on the inside it looks like a normal test file with entries in the following format: 127.0.0.1 localhost. That is, with a structure consisting of the IP address of the domain and its symbolic name, separated by spaces or a tab character.
The example given is a required entry in any such file. It corresponds to the address and name of the user's machine itself. All other entries look similar to this one. With the help of the information placed here, a variety of tasks are solved. For example:
- You can associate the localhost name not with the address of the local machine, but with the address of any computer on the corporate intranet. This is often done by system administrators of enterprises and organizations.
- Similar associations can be used to optimize access to external hosts. If you create a record with a range of IP addresses corresponding to the real addresses of the desired sites, then loading their pages will be faster than when accessing the provider's DNS database.
- Another useful option is the ability to organize the blocking of unwanted domains (for example, domains of advertising sites). To do this, all such domains are assigned the address of the local machine - 127.0.0.1

In principle, hosts is a legacy technology supported for backwards compatibility reasons.
In addition, it has a serious drawback: if the network connection uses an intermediate proxy server, then all storage entries are simply ignored. There are also security issues.
The fact is that many viruses like to delve into the contents of the file and change it at their discretion. One of the recommendations given during a virus attack is to open the file in Notepad and delete from it all entries below the local machine (localhost) entry.
Very often, or after a virus attack, after which, for example, social network to restore access to your page, or after unsuccessful editing, you have to restore the default content. To do this, you need to know what the contents of the original hosts file are. The situation is complicated by the fact that in each operating system from Microsoft Corporation, it is different, although the main thing remains the same. Below is the original contents of the hosts file for some of the currently popular Windows operating systems, which I will list in descending order of their popularity (I personally believe that the most popular system is the newest system. Who says that Windows XP is immortal, and Windows 7 is the most the best creation of Microsoft, people seem to me to be backward in development. I do not want to offend anyone, I will only be glad to hear that I am wrong).
For those who don't know, the Hosts file is used to translate domain names into network . More details about this file are written in the article, the link to which I gave a little higher.
Original Hosts in Windows 8
#
#
#space.
#
#
# For example:
#
#102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com #source server
#38.25.63.10 x.acme.com #x client host
#127.0.0.1 localhost
# :1 localhost
127.0.0.1 localhost
Original Hosts file in Windows 7
# Copyright © 1993–2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1localhost
# :1 localhost
The original Hosts file in the Windows Vista operating system
# Copyright © 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp.
#
#
#space.
#
#
# For example:
#
127.0.0.1 localhost:1 localhost
Original Hosts in Windows XP
# Copyright © 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
#space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
127.0.0.1 localhost
Using the templates provided, you can easily replace the current content of the Hosts file with its original content. In addition to the above files, I would like to clarify a little what is what here. The main content of the original Hosts file in Windows is a commented manual for using this file in English. In addition to describing the functionality of the Hosts file, it also provides various examples of its intended use. And if you still have not figured out where the comments are, and where the functional part of this file is, then get acquainted: the sign # is a special character that means that everything on this line after this character is a comment. And this means that in almost all original Hosts files, the really working part is the last line indicating the loopback interface, which is one of the and point to the computer itself. And based on this, you can completely remove all comments from the Hosts file without losing its performance. That is why the title of the article is Original hosts file in Windows, but not Correct Hosts for Windows. After all, the correct Hosts file will be any rubbish like this:
# In front of you is the most correct of all
# of the most correct Hosts files, which
# ever existed on computers
# on which it has ever been installed
# operating system from famous
# Microsoft Corporation!
127.0.0.1 localhost
# As you can see, comments are everywhere!
# And here,
# and there. But from this hosts file
# does not become wrong!